[ICLR 2024] Large Language Models Are Efficient Learners of Noise-robust Speech Recognition
사전 지식
- LM (Language Model, 언어 모델)
- 단어 sequence의 확률을 결정하기 위한 방법
- 단어를 추론하고 생성
- ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition, 자동 음성인식)
- 음성과 text를 활용하여 학습시킴
- context dependency가 부족할 수 있음
- LM을 연결할 경우 context 정보가 반영되어 성능이 올라감
- Rescoring
- 단어가 나타날 확률을 구할 때 sparsity, long-term dependency 등의 문제가 발생
- 모델에 global context 반영 위해 rescoring 제안
- 여러 번 decoding 거치는 multi-pass 방법론
- 이 논문에는 최상의 N개 결과를 이용하는 N-best list rescoring이 적용됨
- (e.g.) (real) 북구청으로 가세요.
- (e.g.) (top1) 북구청으로 가세요.
- (e.g.) (top2) 북극청으로 가세요.
- (e.g.) (top3) 북구 처음으로 가세요.
- (e.g.) (top4) 부끄청으로 가세요.
- GER (Generative Error Correction)
- noise-robust ASR 모델
- noise가 있는 audio로부터 text를 생성하기 위함
- Beam Search Decoding
- 자연어 처리에서 sequence를 생성할 때 사용하는 기법 중 하나
- 가장 높은 확률의 token 하나를 고르는 게 아니라, 가능도가 높은 여러 개의 token을 선택해 target sequence를 늘리는 방법
- 성능은 좋으나, 속도가 느려질 수 있다는 한계
- KD (Knowledge Distillation, 지식 증류)
- 연산량이 적은 network가 큰 network만큼의 성능을 낼 수 있도록 teacher network의 지식을 student network에 전달하는 학습법
소개
- 최근 연구에서 LLM(Large Language Model)이 NLP(Natural Language Processing)에 자주 사용되고 있음.
- 이 논문은 ASR의 연구 주제 중 하나인 GER에서 N-best list rescoring을 활용하여 성능을 높이고자 함.
- 음성의 noise로 인한 부정적인 영향을 줄이고자 학습된 LLM을 fine-tuning함.
- 저자는 해당 model을 noise에 강인한 RobustGER로 소개하고 있음.
- noise가 낀 audio를 바로 적용하면 corss modality gap으로 인한 성능 저하.
- 이 문제 해결을 위해 noise embedding 추출.
- N-best hypothesis list로부터 noise diversity 측정.
- worse noise condition, beam search decoding 등으로 N-best의 diversity를 높임.
- noise embedding은 language-space denoising을 위한 기법.
- mutual information estimation(KL divergence)을 통한 KD를 사용하여 audio embedding에서 noise information을 제거함.
- WER(word error rate)을 기존 GER 모델보다 53.9% 가량 개선함.
Benchmark 모델 & 데이터
- GER (Generative Error Correction)
- noise에 robust한 ASR 모델
- noisy한 speech $X_n$으로부터 beam search decoding을 활용하여 N_best hypotheses $\mathcal{Y}_N={Y_1,Y_2,···,Y_N}$을 생성함
-
생성한 후보군을 text로 바꿔주는 hypotheses-to-transcription (H2T) 모델에 넣어줌 ${Y=\mathcal{M}_ {H2T}(\mathcal{Y}_N)}$
- ground truth가 $Y^+$일 때, cross-entropy loss를 다음과 같이 계산하여 LLM을 fine-tuning 함. ($\theta$는 learnable parameter) ${\mathcal{L}_ {H2T} = \sum_ {t=1}^{T}- \log \mathcal{P}_ {\theta}(y_ {t}^{+} \vert y_ {t-1}^{+}, ··· ,y_ {1}^{+},\mathcal{Y}_ {N})}$
- 데이터
- noise한 speech audio 사용
- CHiME-4, DEMAND, NOIZEUS, LibriSpeech-FreeSound, RATS, etc.
- noise한 speech audio 사용
방법론
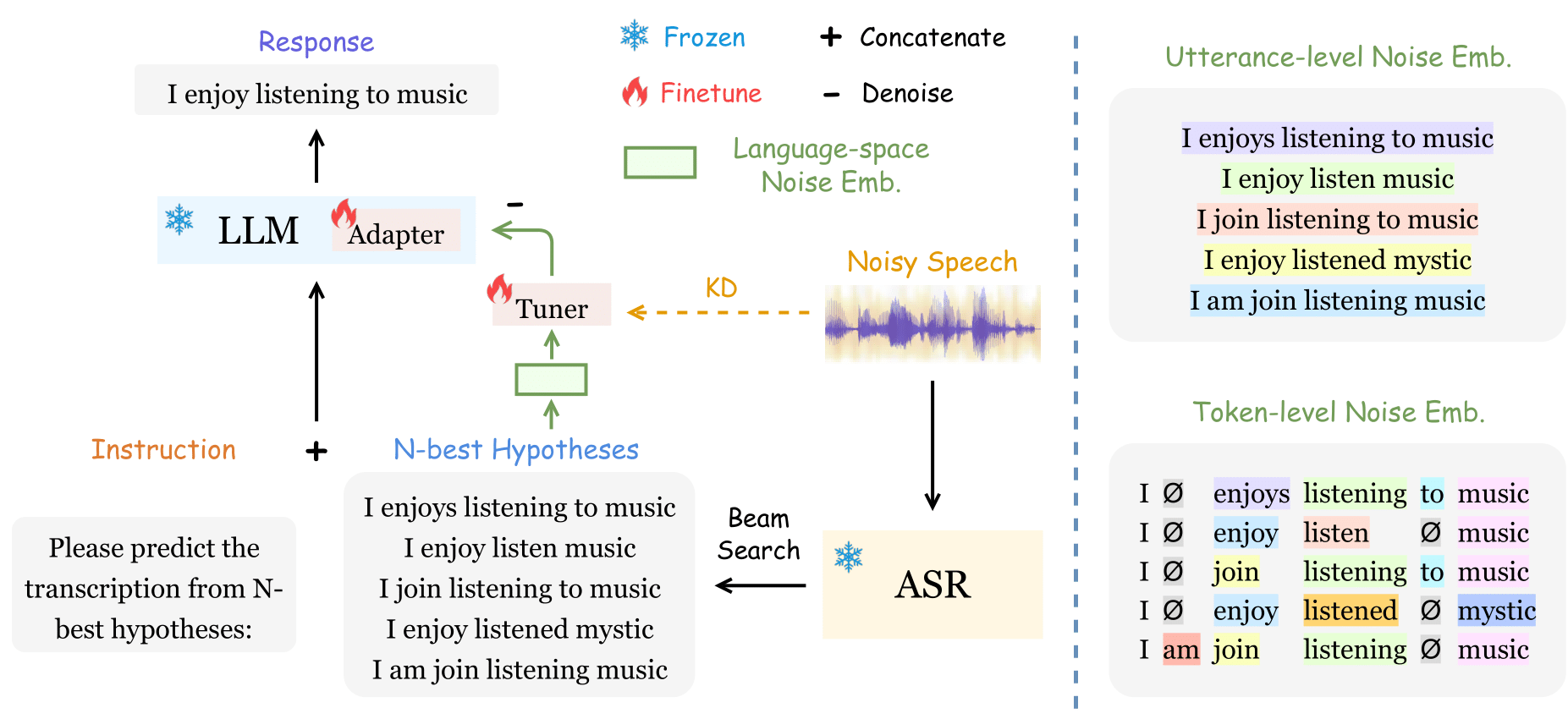
- 전체 Framework
- $\mathcal{Y}_ {N}$에서 $N=5$로 설정
- $\mathcal{Y}_ {N}$으로부터 추출한 language-space noise를 $E_ {LN}$으로 설정
- source speech $X_n$에서 KD를 통해 noise를 제거하기 위해 ASR audio embedding을 $\mathcal{E}_ {ASR}(X_ {n})$으로 설정
- noise 제거를 위해 denoising을 minus sign을 붙여 $-E_ {LN}$으로 표현
- 다음 ${\mathcal{M}_ {H2T}}$는 LLM finetuning을 거친 H2T mapping: ${Y=\mathcal{M}_ {H2T}(\mathcal{Y}_ {N};-E_ {LN})}$
- Language-space Noise Embedding
- $E_ {LN}=[E_ {LN}^{utt};E_ {LN}^{tok}]$
- $E_ {LN}$은 N-best list 내부의 문장 전체 diversity에 영향 끼치는 1) utterance level $E_ {LN}^{utt}$와 단어 단위에서 distribution을 측정한 2) token level $E_ {LN}^{tok}$로 나누어짐
- 한편, raw text로부터 audio embedding을 얻기 위해 sentence-BERT (SBERT)가 사용됨
- Utterance-level Noise Embedding
-
Utterance-level Noise Embedding은 음성 신호에서 발생하는 배경 소음이나 잡음을 표현하는 데 사용되는 특징 벡터
-
$E_ {LN}^{utt}=Concat { [\mathcal{E}_ {sbert} (Y_ {i}) - \mathcal{E}_ {sbert}(Y_ {j}) ]_ {i,j=1,i>j}^{N} } \in \mathbb{R}^{ {N(N-1)\over{2} } \times D_ {sbert} }$
- 이 때, $D_ {sbert}$는 SBERT embedding size
- $i,j$ 차이가 클 수록, worse noise가 생성됨
-
- Token-level Noise Embedding
- Token-level Noise Embedding은특정 단어나 음성 토큰에 대응되는 잡음이나 변형을 나타내는 임베딩 벡터
- zero-padding ($Ø$)한 $Y_ {i}$를 일정한 길이로 잘라 $T$개의 token을 만듦
- $Y_i^{ali}=[y_ {i_ {1}}^{ali},y_ {i_ {2}}^{ali},···,y_ {i_ {T}}^{ali}], \quad y_ {i_ {t}}^{ali}\in \mathcal{V} \cup Ø$
- $E_ {edit}$을 통해 token-level difference를 측정
- $E_ {LN}^{tok} = Concat { [ E_ {edit}(Y_ {i}^{ali}, Y_ {j}^{ali}) ]_ {i,j=1,i>j}^{N} } \in \mathbb{R}^{ {N(N-1)\over{2}} \times D_ {sbert} }$
- $E_ {edit}(Y_i^{ali},Y_j^{ali})=\sum_ {t=1}^T[\mathcal{E}_ {sbert}(y_ {i_t}^{ali})-\mathcal{E}_ {sbert}(y_ {j_t}^{ali})]$
- Audio Noise Distillation
- Mutual Information을 활용하여 clean speech와 noisy speech의 분포가 얼마나 차이 나는지 살핌
- $I(X;Z)=D_ {KL}(\mathbb{P}_ {XZ} \vert\vert\mathbb{P}_ {X} \mathbb{P}_ {Z})$
- MINE (mutual information neural estimation)
- MINE은 상호 정보(Mutual Information, MI)를 신경망을 통해 추정하는 방법론
- 아래와 같은 MINE (mutual information neural estimation)을 활용하여 parameter $\theta \in \Theta$에 대해 계산
- $\psi_ { \mathbf{\theta} }는 \mathcal{X} \times \mathcal{Z} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ statistics network
- $I_ {\Theta}(X;Z) = \sup_ {\theta \in \Theta} \mathbb{E}_ {\mathbb{P}_ {XZ}}[ \psi_ { \mathbf{\theta} } ] - \log(\mathbb{E}_ {\mathbb{P}_ {X} \mathbb{P}_ {Z}}[e^{\psi_ { \mathbf{\theta} } } ])$
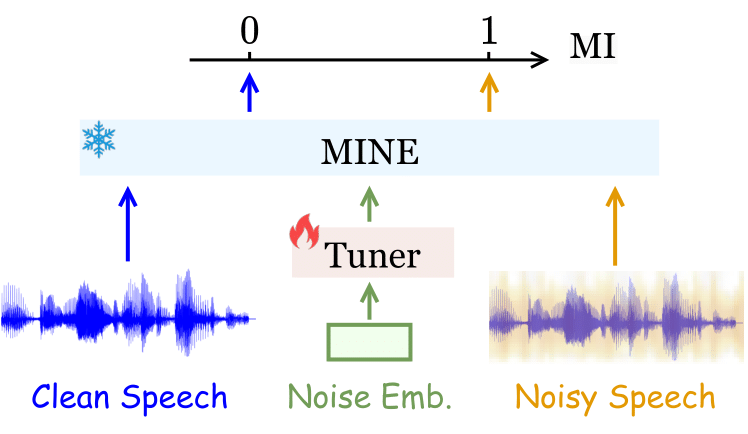
- 학습 알고리즘은 아래와 같음
- 이 알고리즘은 잡음이 섞인 음성 데이터를 효과적으로 처리하여 깨끗한 음성 데이터를 얻기 위해 여러 모델과 네트워크를 조정하는 과정을 반복
- Require:
- LLM $\mathcal{M}_ {\text{H2T}}$ 과 어댑터 $\mathcal{G}_ { \mathbf{\upsilon} }$
- 정보 이론 기반의 MINE 통계 네트워크 $\psi$ (parameters: $\mathbf\theta$)
- 언어 임베딩 조정 튜너 $\mathcal{T}$ (parameters: $\mathbf{\omega}$)
- N-best 음성 인식 가설 $\mathcal{Y}_N$
- 병렬 잡음 음성 $\mathcal{X}_ {n}$ 및 깨끗한 음성 데이터 $\mathcal{X}_ {c}$
- 배치 크기 $B$ 와 총 반복 횟수 $M$
- 하이퍼 파라미터 가중치 $\lambda$ (손실 함수 가중치) -
- For $m=1$ to $M$:
- N-best 가설 샘플링: ${ \mathcal{Y}_ {N}^{(1)}, \mathcal{Y}_ {N}^{(2)}, \cdots, \mathcal{Y}_ {N}^{(B)} }$;
- 잡음 및 깨끗한 음성 샘플 추출: ${(X_n^{(1)}, X_c^{(1)}), (X_n^{(2)}, X_c^{(2)}), \cdots, (X_n^{(B)}, X_c^{(B)})}$;
- 언어 공간 잡음 임베딩 추출: ${E_ {\text{LN}}^{(1)}, E_ {\text{LN}}^{(2)}, \cdots, E_ {\text{LN}}^{(B)}}$;
- 상호 정보 계산: $\mathcal{I} = \frac{1}{B} \sum_ {b=1}^{B} \psi_ {\mathbf{\theta}} (E_ {\text{LN}}^{(b)}, \mathcal{E}_ {\text{ASR}}(X_ {n}^{(b)})) - \log( \frac{1}{B} \sum_ {b=1}^{B} e^{\psi_ { \mathbf{\theta} }(E_ {\text{LN}}^{(b)}, \mathcal{E}_ {\text{ASR}}(X_ {c}^{(b)}))})$;
- 파라미터 업데이트: $\mathbf{\theta} \leftarrow \mathbf{\theta} + {\mathbf{g}}_ {\mathbf{\theta}}$; (${\mathbf{g}}_ { \mathbf{\theta} } = \nabla_ { \mathbf{\theta} }(\mathcal{I})$)
- GER 손실 함수 계산: $\mathcal{L}_ {\text{H2T}}$ (with $\mathcal{T}_ {\mathbf{\omega}} (E_ {\text{LN}}^{(b)})$);
- 상호 정보 재계산: $\mathcal{I}_ {1} = \frac{1}{B}\sum_ {b=1}^{B} \psi_ {\mathbf{\theta}}(\mathcal{T}_ {\mathbf{\omega}}(E_ {\text{LN}}^{(b)}), \mathcal{E}_ {\text{ASR}}(X_ {n}^{(b)}))$;
- 파라미터 업데이트: $\mathbf{\upsilon} \leftarrow \mathbf{\upsilon} - \mathbf{g_ {\upsilon}}, \mathbf{\omega} \leftarrow \mathbf{\omega} - \mathbf{g_ {\omega}}$; ($\mathbf{g_ {\upsilon,\omega}} = \nabla_ {\mathbf{\upsilon,\omega}}(\mathcal{L}_ {\text{H2T}} - \lambda \mathcal{I}_ {1})$ )
실험
- 다양한 noise 환경의 audio에 대해 실험을 진행함
- GER은 baseline에 비해 성능 진전이 있었지만 여러 잡음 조건에 대해 성능 향상 제한적
- RobustGER은 여러 소음에 대한 일관된 성능 향상 (Table 1)
- RobustGER은 소음 정도에 대해서도 일관된 성능 향상 (Table 2)
-
token-level noise가 성능 개선에 큰 기여 (Table 3)
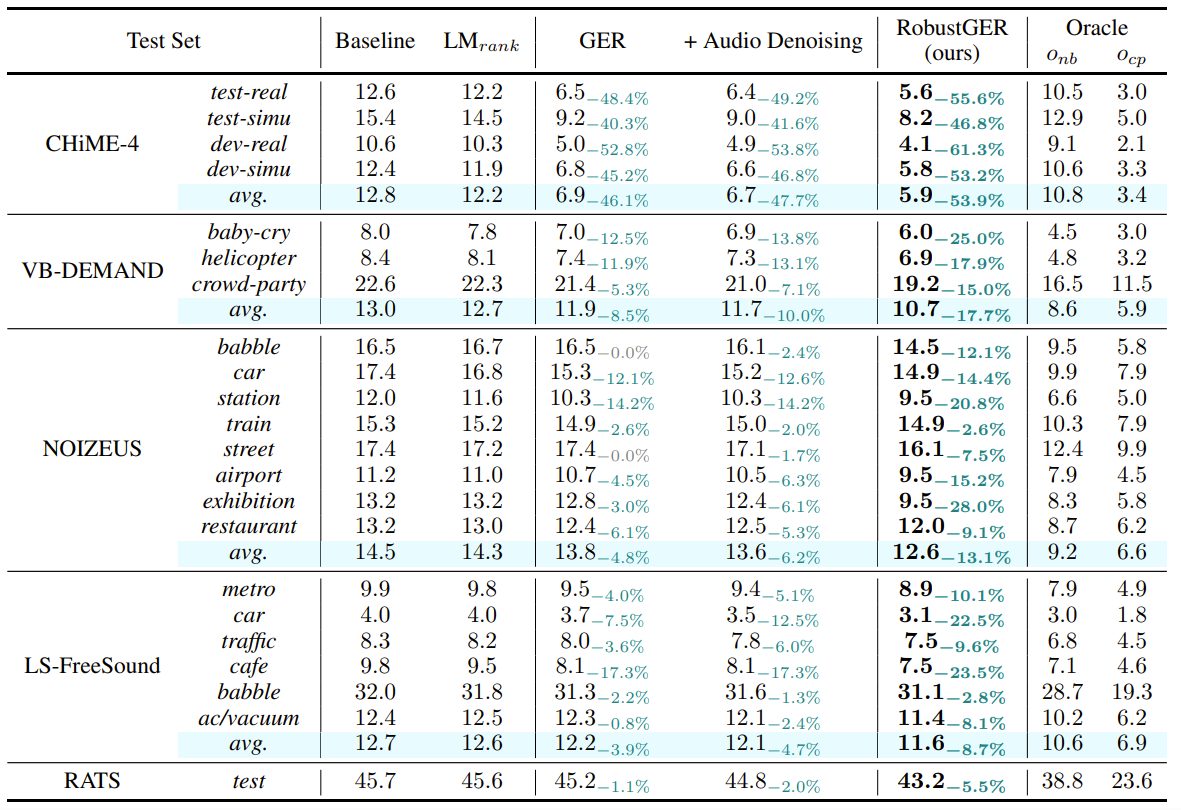
$\quad$ Table 1: WER (%) results of RobustGER with LLaMA-2-7b finetuning
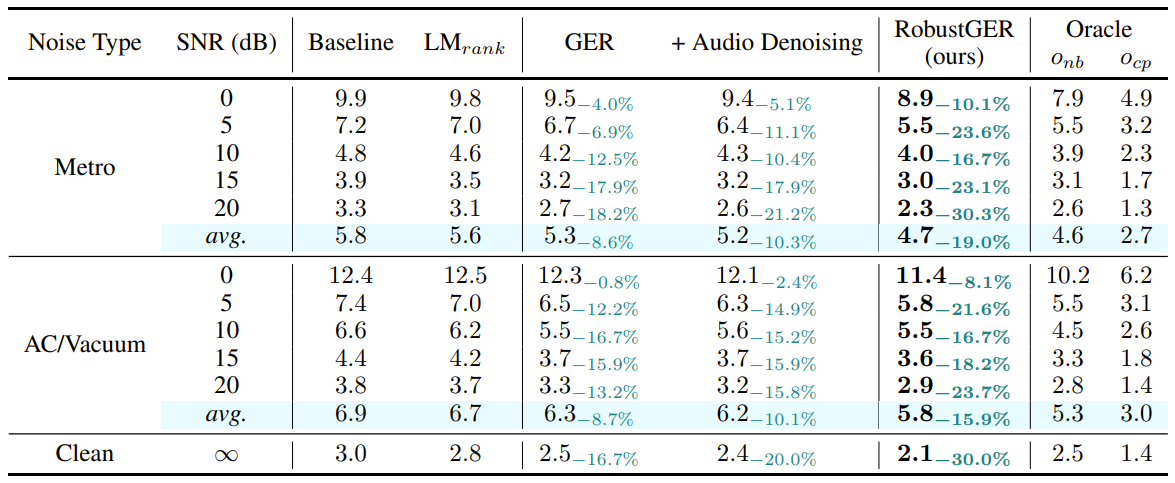
$\quad$ Table 2: WER (%) results of RobustGER on different SNR-level testing conditions
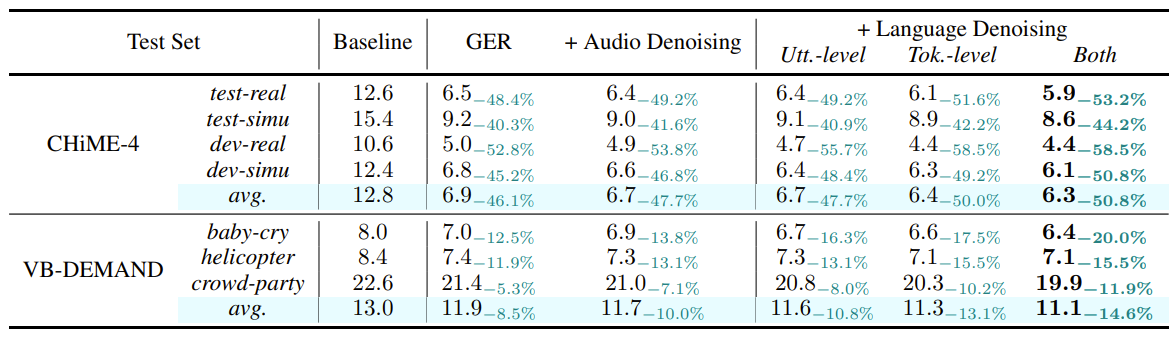
$\quad$ Table 3: Ablation study of the language-space noise embedding in terms of utterance and token levels
- noise embedding
- KD 방식을 통해 최적의 noise embedding을 구함
-
다음과 같이 잡음의 대표성이 잘 나타남
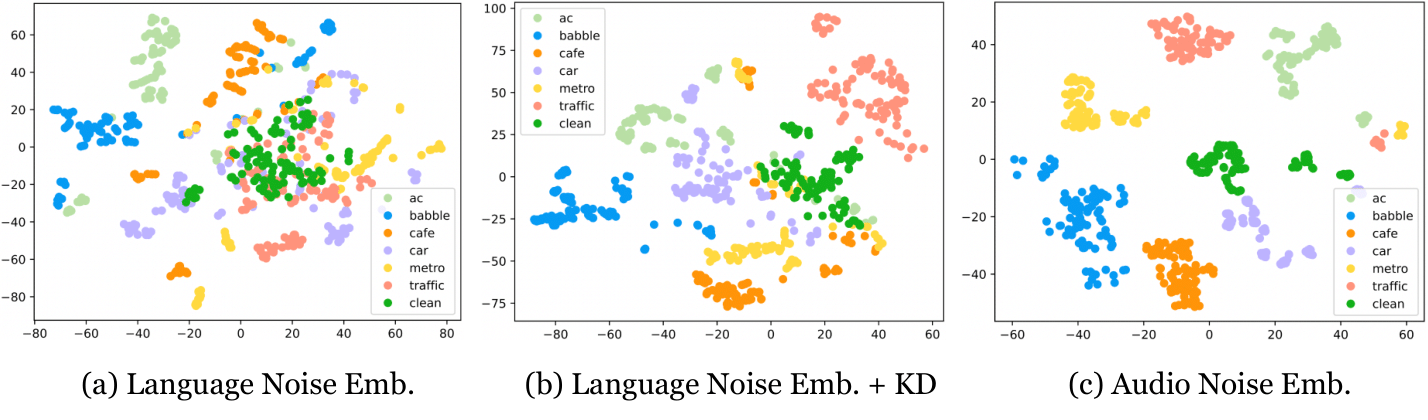
- 데이터 효율성
-
LLM fine-tuning을 활용하여 점진적으로 훈련 데이터 크기를 줄여도 WER 유지
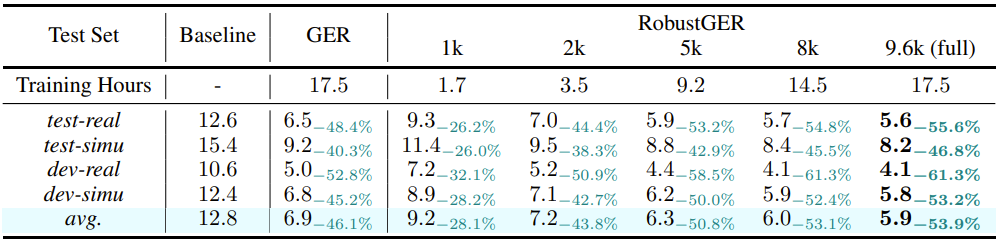
$\quad$ Table 4: Data efficiency of RobustGER on CHiME-4 test sets
-
- error 수정 예시
-
다음과 같이 RobustGER이 correction 성능이 가장 뛰어난 것을 볼 수 있음
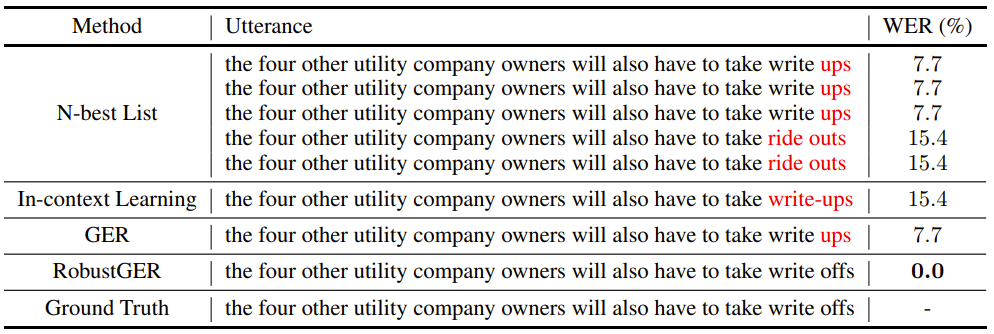
$\quad$ Table 5: Case study of RobustGER
-
결론
- language-space noise embedding을 추출하여 이를 denoising 해주었을 때, word correction 성능이 향상되는 것을 볼 수 있었음
- noise를 인식하고 noise embedding을 생성하는 복합적인 알고리즘을 활용하였음
- speech 분야에서 fine-tuning LLM의 우수한 성능을 보여줌
저자
- Yuchen Hu (yuchen005@e.ntu.edu.sg)
- Chen Chen (hucky@nvidia.com)
참조
- Github link (https://github.com/YUCHEN005/RobustGER)